Are 3D-Printed Homes About to Revolutionize Residential Construction?
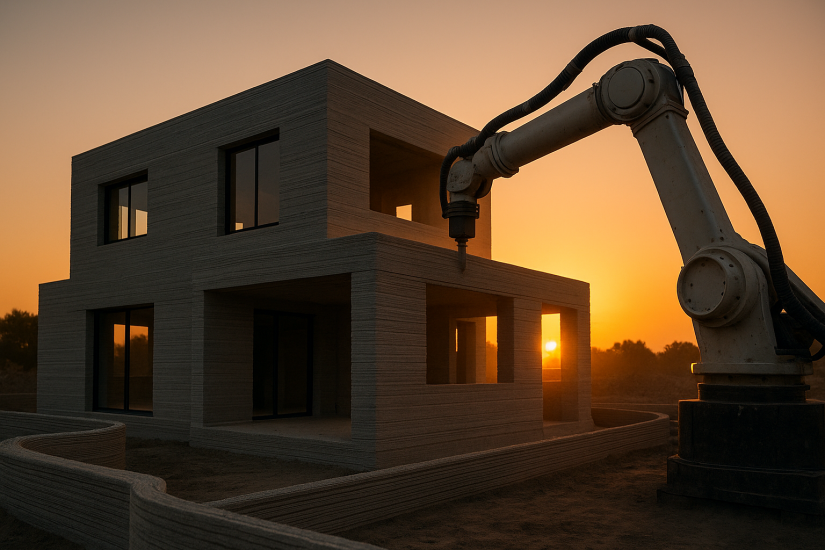

3D-printed homes have taken the construction world by storm in the last 24 hours, capturing headlines with new pilot projects from Austin, Texas, to Dubbo, Australia. This surge in attention reflects growing interest in additive manufacturing’s promise to cut build times, reduce waste, and lower costs—trends likely to persist through the coming week and beyond.
What Are 3D-Printed Homes?
At their core, 3D-printed homes are structures assembled layer by layer by a robotic extruder that deposits specialized concrete or composite “inks.” Guided by digital blueprints, these giant printers carve out walls, niches, and even built-in fixtures without traditional formwork. Unlike modular builds, the process creates continuous, monolithic shells—delivering precision and design flexibility that conventional methods can’t match.
Advantages of 3D-Printed Construction
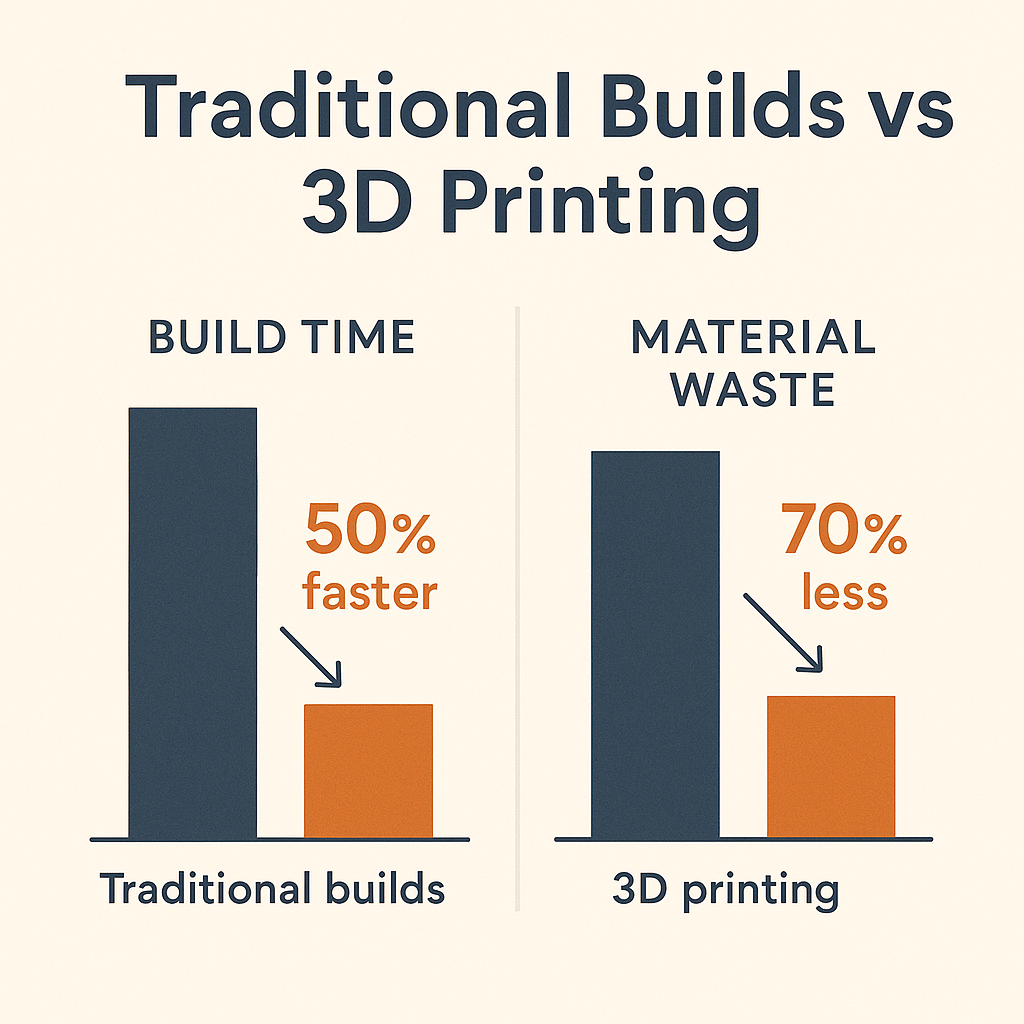
Speed and Efficiency
Traditional stick-built homes can take months; some 3D-print systems can finish a small residence in under 48 hours. This dramatic acceleration stems from automated layering and minimal on-site labor.
Sustainability and Waste Reduction
By extruding material only where it’s needed, 3D printing slashes construction waste by up to 70%. Excess concrete from conventional pours often goes to landfill, whereas additive processes recycle unspent material directly back into the feeder system. SkyQuest
Cost Savings
Labor accounts for nearly 30% of build costs; robotics can reduce crew requirements significantly. Early pilot projects report savings of 20–40% on overall expenses, making affordable housing initiatives more feasible. MySA
Key Technologies Driving the Trend
- Extrusion Robotics: Advanced gantry-style printers with multi-axis arms deliver precise layer placement.
- Specialized Mortars: Tailored mixes cure quickly and bond layer-to-layer, sometimes incorporating recycled aggregates for green builds.
- BIM Integration: Digital models feed directly into printers, enabling complex geometries and MEP (mechanical, electrical, plumbing) embeds mid-print.
Case Study: Austin’s Mueller Neighborhood
ICON, a leading additive construction firm, recently unveiled three one-bedroom 650 sq ft homes for sale under the Mueller Affordable Homes Program in Austin, Texas. These units demonstrate how 3D printing can deliver quality dwellings within weeks rather than months—fueling local buzz and pre-sale interest among income-qualified buyers. MySA
Challenges and Considerations
- Regulatory Hurdles: Building codes vary by jurisdiction; standardizing inspections for layer-by-layer methods remains a work in progress.
- Material Performance: Long-term durability and insulation R-values require further validation, especially in extreme climates.
- Scale Limitations: Current printers excel at small to mid-sized homes; scaling to multi-story structures demands larger machines and more robust engineering. News.com.au
The Road Ahead for 3D-Printed Homes
With governments and developers eyeing rapid, cost-effective solutions to housing shortages, additive construction is poised for wider adoption. Pilot projects in Europe, Asia, and Australia are already scaling up to multi-unit and public housing deployments, signaling that what began as a curiosity will soon form a core pillar of sustainable, affordable residential construction. Daily Telegraph
Conclusion and Call-to-Action
As 3D-printed homes transition from experimental to mainstream, construction professionals and homeowners alike must stay informed on material innovations, code developments, and project case studies.
Interested in leveraging 3D printing for your next project? Contact our team today to explore turnkey solutions that deliver faster builds, lower costs, and greener footprints.